In questo tutorial imparerai cos'è un albero avl. Inoltre, troverai esempi funzionanti di varie operazioni eseguite su un albero avl in C, C ++, Java e Python.
L'albero AVL è un albero di ricerca binario autobilanciato in cui ogni nodo mantiene informazioni aggiuntive chiamate fattore di equilibrio il cui valore è -1, 0 o +1.
L'albero AVL ha preso il nome dal suo inventore Georgy Adelson-Velsky e Landis.
Fattore di equilibrio
Il fattore di bilanciamento di un nodo in un albero AVL è la differenza tra l'altezza della sottostruttura sinistra e quella della sottostruttura destra di quel nodo.
Fattore di bilanciamento = (Altezza sottostruttura sinistra - Altezza sottostruttura destra) o (Altezza sottostruttura destra - Altezza sottostruttura sinistra)
La proprietà di autobilanciamento di un albero avl è mantenuta dal fattore di equilibrio. Il valore del fattore di bilanciamento dovrebbe sempre essere -1, 0 o +1.
Un esempio di albero avl bilanciato è:
 Albero Avl
Albero Avl
Operazioni su un albero AVL
Diverse operazioni che possono essere eseguite su un albero AVL sono:
Rotazione delle sottostrutture in un albero AVL
Durante l'operazione di rotazione, le posizioni dei nodi di una sottostruttura vengono scambiate.
Esistono due tipi di rotazioni:
Ruota a sinistra
Nella rotazione sinistra, la disposizione dei nodi a destra viene trasformata nelle disposizioni sul nodo sinistro.
Algoritmo
- Lascia che l'albero iniziale sia:
 Ruota a sinistra
Ruota a sinistra - Se y ha un sottoalbero sinistro, assegna x come genitore del sottoalbero sinistro di y.
 Assegna x come genitore del sottoalbero sinistro di y
Assegna x come genitore del sottoalbero sinistro di y - Se il genitore di x è
NULL, rendi y come radice dell'albero. - Altrimenti se x è il figlio sinistro di p, rendi y il figlio sinistro di p.
- Altrimenti assegna y come figlio destro di p.
 Cambia il genitore di x in quello di y
Cambia il genitore di x in quello di y - Rendi y come genitore di x.
 Assegna y come genitore di x.
Assegna y come genitore di x.
Ruota a destra
Nella rotazione a sinistra, la disposizione dei nodi a sinistra viene trasformata nelle disposizioni sul nodo di destra.
- Sia l'albero iniziale:
 albero iniziale
albero iniziale - Se x ha un sottoalbero destro, assegna y come genitore del sottoalbero destro di x.
 Assegna y come genitore del sottoalbero destro di x
Assegna y come genitore del sottoalbero destro di x - Se il genitore di y è
NULL, rendi x come radice dell'albero. - Altrimenti se y è il figlio destro del suo genitore p, rendi x il figlio destro di p.
- Altrimenti assegna x come figlio sinistro di p.
 Assegna il genitore di y come genitore di x.
Assegna il genitore di y come genitore di x. - Rendi x il genitore di y.
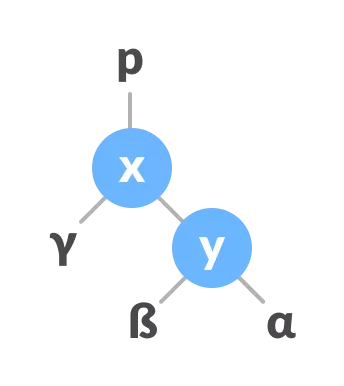 Assegna x come genitore di y
Assegna x come genitore di y
Ruota sinistra-destra e destra-sinistra
Nella rotazione sinistra-destra, le disposizioni vengono prima spostate a sinistra e poi a destra.
- Esegui la rotazione a sinistra su xy.
 Ruota a sinistra xy
Ruota a sinistra xy - Fai la giusta rotazione su yz.
 Ruota a destra zy
Ruota a destra zy
Nella rotazione destra-sinistra, le disposizioni vengono prima spostate a destra e poi a sinistra.
- Fai la rotazione a destra su xy.
 Ruota a destra xy
Ruota a destra xy - Esegui la rotazione a sinistra su zy.
 Ruota a sinistra zy
Ruota a sinistra zy
Algoritmo per inserire un newNode
Un newNode viene sempre inserito come nodo foglia con fattore di bilanciamento uguale a 0.
- Sia l'albero iniziale:
 Albero iniziale per l'inserimento
Albero iniziale per l'inserimento
Sia il nodo da inserire: Nuovo nodo
Nuovo nodo - Vai al nodo foglia appropriato per inserire un newNode utilizzando i seguenti passaggi ricorsivi. Confronta newKey con rootKey dell'albero corrente.
- Se newKey <rootKey, chiama l'algoritmo di inserimento nella sottostruttura sinistra del nodo corrente finché non viene raggiunto il nodo foglia.
- Altrimenti, se newKey> rootKey, chiama l'algoritmo di inserimento sulla sottostruttura destra del nodo corrente fino a raggiungere il nodo foglia.
- Altrimenti, restituisci leafNode.
 Trovare la posizione in cui inserire newNode
Trovare la posizione in cui inserire newNode
- Confronta leafKey ottenuto dai passaggi precedenti con newKey:
- Se newKey <leafKey, crea newNode come leftChild di leafNode.
- Altrimenti, crea newNode come rightChild di leafNode.
 Inserimento del nuovo nodo
Inserimento del nuovo nodo
- Aggiorna balanceFactor dei nodi.
 Aggiornamento del fattore di bilanciamento dopo l'inserimento
Aggiornamento del fattore di bilanciamento dopo l'inserimento - Se i nodi sono sbilanciati, riequilibrare il nodo.
- Se balanceFactor> 1, significa che l'altezza della sottostruttura sinistra è maggiore di quella della sottostruttura destra. Quindi, fai una rotazione a destra o sinistra-destra
- Se newNodeKey <leftChildKey esegue la rotazione a destra.
- Altrimenti, fai la rotazione sinistra-destra.
 Bilanciamento dell'albero con rotazione
Bilanciamento dell'albero con rotazione 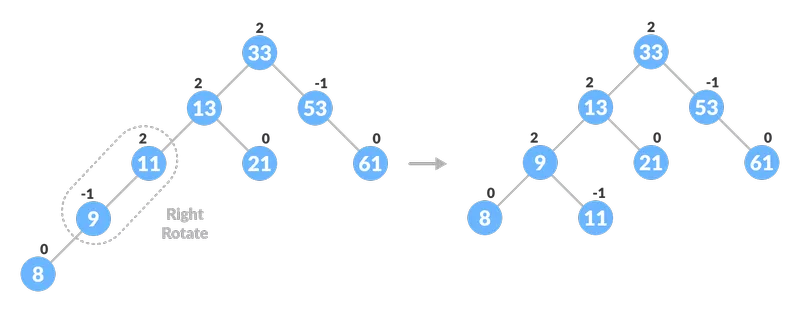 Bilanciamento dell'albero con rotazione
Bilanciamento dell'albero con rotazione
- Se balanceFactor <-1, significa che l'altezza della sottostruttura destra è maggiore di quella della sottostruttura sinistra. Quindi, fai la rotazione a destra o la rotazione da destra a sinistra
- Se newNodeKey> rightChildKey esegue la rotazione a sinistra.
- Altrimenti, fai la rotazione da destra a sinistra
- Se balanceFactor> 1, significa che l'altezza della sottostruttura sinistra è maggiore di quella della sottostruttura destra. Quindi, fai una rotazione a destra o sinistra-destra
- L'albero finale è:
 Albero bilanciato finale
Albero bilanciato finale
Algoritmo per eliminare un nodo
Un nodo viene sempre eliminato come nodo foglia. Dopo aver eliminato un nodo, i fattori di equilibrio dei nodi vengono modificati. Al fine di riequilibrare il fattore di equilibrio vengono eseguite opportune rotazioni.
- Individua nodeToBeDeleted (la ricorsione viene utilizzata per trovare nodeToBeDeleted nel codice utilizzato di seguito).
 Individuazione del nodo da eliminare
Individuazione del nodo da eliminare - Esistono tre casi per eliminare un nodo:
- Se nodeToBeDeleted è il nodo foglia (cioè non ha alcun figlio), rimuovere nodeToBeDeleted.
- Se nodeToBeDeleted ha un figlio, sostituisci il contenuto di nodeToBeDeleted con quello del figlio. Rimuovi il bambino.
- Se nodeToBeDeleted ha due figli, trova il successore inorder w di nodeToBeDeleted (cioè nodo con un valore minimo di chiave nella sottostruttura destra).
 Trovare il successore
Trovare il successore
- Sostituisci il contenuto di nodeToBeDeleted con quello di w.
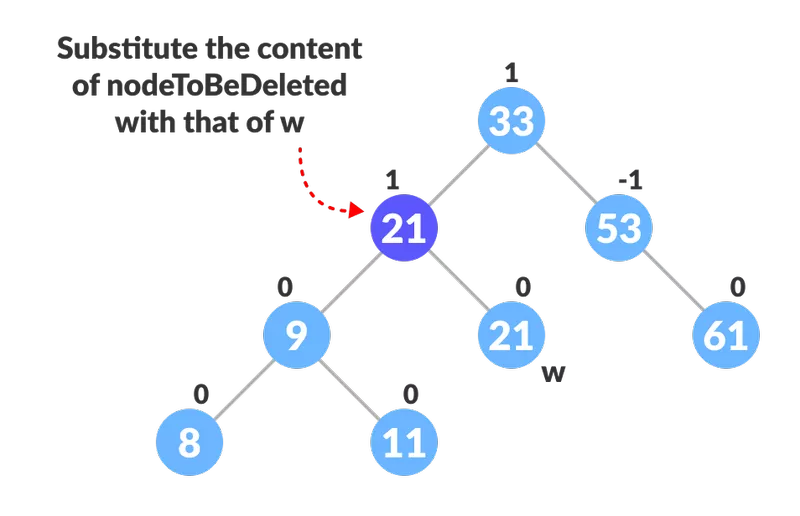 Sostituisci il nodo da eliminare
Sostituisci il nodo da eliminare - Rimuovere il nodo foglia w.
 Rimuovi w
Rimuovi w
- Sostituisci il contenuto di nodeToBeDeleted con quello di w.
- Aggiorna balanceFactor dei nodi.
 Aggiorna bf
Aggiorna bf - Riequilibrare l'albero se il fattore di bilanciamento di uno dei nodi non è uguale a -1, 0 o 1.
- Se balanceFactor of currentNode> 1,
- Se balanceFactor di leftChild> = 0, eseguire la rotazione a destra.
 Ruota a destra per bilanciare l'albero
Ruota a destra per bilanciare l'albero - Altrimenti fai la rotazione sinistra-destra.
- Se balanceFactor di leftChild> = 0, eseguire la rotazione a destra.
- Se balanceFactor of currentNode <-1,
- Se balanceFactor di rightChild <= 0, effettua la rotazione a sinistra.
- Altrimenti fai la rotazione da destra a sinistra.
- Se balanceFactor of currentNode> 1,
- L'albero finale è:
 Avl tree final
Avl tree final
Esempi di Python, Java e C / C ++
Python Java C C ++ # AVL tree implementation in Python import sys # Create a tree node class TreeNode(object): def __init__(self, key): self.key = key self.left = None self.right = None self.height = 1 class AVLTree(object): # Function to insert a node def insert_node(self, root, key): # Find the correct location and insert the node if not root: return TreeNode(key) elif key 1: if key < root.left.key: return self.rightRotate(root) else: root.left = self.leftRotate(root.left) return self.rightRotate(root) if balanceFactor root.right.key: return self.leftRotate(root) else: root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right) return self.leftRotate(root) return root # Function to delete a node def delete_node(self, root, key): # Find the node to be deleted and remove it if not root: return root elif key root.key: root.right = self.delete_node(root.right, key) else: if root.left is None: temp = root.right root = None return temp elif root.right is None: temp = root.left root = None return temp temp = self.getMinValueNode(root.right) root.key = temp.key root.right = self.delete_node(root.right, temp.key) if root is None: return root # Update the balance factor of nodes root.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(root.left), self.getHeight(root.right)) balanceFactor = self.getBalance(root) # Balance the tree if balanceFactor> 1: if self.getBalance(root.left)>= 0: return self.rightRotate(root) else: root.left = self.leftRotate(root.left) return self.rightRotate(root) if balanceFactor < -1: if self.getBalance(root.right) <= 0: return self.leftRotate(root) else: root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right) return self.leftRotate(root) return root # Function to perform left rotation def leftRotate(self, z): y = z.right T2 = y.left y.left = z z.right = T2 z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) return y # Function to perform right rotation def rightRotate(self, z): y = z.left T3 = y.right y.right = z z.left = T3 z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) return y # Get the height of the node def getHeight(self, root): if not root: return 0 return root.height # Get balance factore of the node def getBalance(self, root): if not root: return 0 return self.getHeight(root.left) - self.getHeight(root.right) def getMinValueNode(self, root): if root is None or root.left is None: return root return self.getMinValueNode(root.left) def preOrder(self, root): if not root: return print("(0) ".format(root.key), end="") self.preOrder(root.left) self.preOrder(root.right) # Print the tree def printHelper(self, currPtr, indent, last): if currPtr != None: sys.stdout.write(indent) if last: sys.stdout.write("R----") indent += " " else: sys.stdout.write("L----") indent += "| " print(currPtr.key) self.printHelper(currPtr.left, indent, False) self.printHelper(currPtr.right, indent, True) myTree = AVLTree() root = None nums = (33, 13, 52, 9, 21, 61, 8, 11) for num in nums: root = myTree.insert_node(root, num) myTree.printHelper(root, "", True) key = 13 root = myTree.delete_node(root, key) print("After Deletion: ") myTree.printHelper(root, "", True)
// AVL tree implementation in Java // Create node class Node ( int item, height; Node left, right; Node(int d) ( item = d; height = 1; ) ) // Tree class class AVLTree ( Node root; int height(Node N) ( if (N == null) return 0; return N.height; ) int max(int a, int b) ( return (a> b) ? a : b; ) Node rightRotate(Node y) ( Node x = y.left; Node T2 = x.right; x.right = y; y.left = T2; y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) + 1; x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) + 1; return x; ) Node leftRotate(Node x) ( Node y = x.right; Node T2 = y.left; y.left = x; x.right = T2; x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) + 1; y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) + 1; return y; ) // Get balance factor of a node int getBalanceFactor(Node N) ( if (N == null) return 0; return height(N.left) - height(N.right); ) // Insert a node Node insertNode(Node node, int item) ( // Find the position and insert the node if (node == null) return (new Node(item)); if (item node.item) node.right = insertNode(node.right, item); else return node; // Update the balance factor of each node // And, balance the tree node.height = 1 + max(height(node.left), height(node.right)); int balanceFactor = getBalanceFactor(node); if (balanceFactor> 1) ( if (item node.left.item) ( node.left = leftRotate(node.left); return rightRotate(node); ) ) if (balanceFactor node.right.item) ( return leftRotate(node); ) else if (item < node.right.item) ( node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); ) ) return node; ) Node nodeWithMimumValue(Node node) ( Node current = node; while (current.left != null) current = current.left; return current; ) // Delete a node Node deleteNode(Node root, int item) ( // Find the node to be deleted and remove it if (root == null) return root; if (item root.item) root.right = deleteNode(root.right, item); else ( if ((root.left == null) || (root.right == null)) ( Node temp = null; if (temp == root.left) temp = root.right; else temp = root.left; if (temp == null) ( temp = root; root = null; ) else root = temp; ) else ( Node temp = nodeWithMimumValue(root.right); root.item = temp.item; root.right = deleteNode(root.right, temp.item); ) ) if (root == null) return root; // Update the balance factor of each node and balance the tree root.height = max(height(root.left), height(root.right)) + 1; int balanceFactor = getBalanceFactor(root); if (balanceFactor> 1) ( if (getBalanceFactor(root.left)>= 0) ( return rightRotate(root); ) else ( root.left = leftRotate(root.left); return rightRotate(root); ) ) if (balanceFactor < -1) ( if (getBalanceFactor(root.right) <= 0) ( return leftRotate(root); ) else ( root.right = rightRotate(root.right); return leftRotate(root); ) ) return root; ) void preOrder(Node node) ( if (node != null) ( System.out.print(node.item + " "); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); ) ) // Print the tree private void printTree(Node currPtr, String indent, boolean last) ( if (currPtr != null) ( System.out.print(indent); if (last) ( System.out.print("R----"); indent += " "; ) else ( System.out.print("L----"); indent += "| "; ) System.out.println(currPtr.item); printTree(currPtr.left, indent, false); printTree(currPtr.right, indent, true); ) ) // Driver code public static void main(String() args) ( AVLTree tree = new AVLTree(); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 33); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 13); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 53); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 9); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 21); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 61); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 8); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 11); tree.printTree(tree.root, "", true); tree.root = tree.deleteNode(tree.root, 13); System.out.println("After Deletion: "); tree.printTree(tree.root, "", true); ) )
// AVL tree implementation in C #include #include // Create Node struct Node ( int key; struct Node *left; struct Node *right; int height; ); int max(int a, int b); // Calculate height int height(struct Node *N) ( if (N == NULL) return 0; return N->height; ) int max(int a, int b) ( return (a> b) ? a : b; ) // Create a node struct Node *newNode(int key) ( struct Node *node = (struct Node *) malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); node->key = key; node->left = NULL; node->right = NULL; node->height = 1; return (node); ) // Right rotate struct Node *rightRotate(struct Node *y) ( struct Node *x = y->left; struct Node *T2 = x->right; x->right = y; y->left = T2; y->height = max(height(y->left), height(y->right)) + 1; x->height = max(height(x->left), height(x->right)) + 1; return x; ) // Left rotate struct Node *leftRotate(struct Node *x) ( struct Node *y = x->right; struct Node *T2 = y->left; y->left = x; x->right = T2; x->height = max(height(x->left), height(x->right)) + 1; y->height = max(height(y->left), height(y->right)) + 1; return y; ) // Get the balance factor int getBalance(struct Node *N) ( if (N == NULL) return 0; return height(N->left) - height(N->right); ) // Insert node struct Node *insertNode(struct Node *node, int key) ( // Find the correct position to insertNode the node and insertNode it if (node == NULL) return (newNode(key)); if (key key) node->left = insertNode(node->left, key); else if (key> node->key) node->right = insertNode(node->right, key); else return node; // Update the balance factor of each node and // Balance the tree node->height = 1 + max(height(node->left), height(node->right)); int balance = getBalance(node); if (balance> 1 && key left->key) return rightRotate(node); if (balance node->right->key) return leftRotate(node); if (balance> 1 && key> node->left->key) ( node->left = leftRotate(node->left); return rightRotate(node); ) if (balance < -1 && key right->key) ( node->right = rightRotate(node->right); return leftRotate(node); ) return node; ) struct Node *minValueNode(struct Node *node) ( struct Node *current = node; while (current->left != NULL) current = current->left; return current; ) // Delete a nodes struct Node *deleteNode(struct Node *root, int key) ( // Find the node and delete it if (root == NULL) return root; if (key key) root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key); else if (key> root->key) root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key); else ( if ((root->left == NULL) || (root->right == NULL)) ( struct Node *temp = root->left ? root->left : root->right; if (temp == NULL) ( temp = root; root = NULL; ) else *root = *temp; free(temp); ) else ( struct Node *temp = minValueNode(root->right); root->key = temp->key; root->right = deleteNode(root->right, temp->key); ) ) if (root == NULL) return root; // Update the balance factor of each node and // balance the tree root->height = 1 + max(height(root->left), height(root->right)); int balance = getBalance(root); if (balance> 1 && getBalance(root->left)>= 0) return rightRotate(root); if (balance> 1 && getBalance(root->left) left = leftRotate(root->left); return rightRotate(root); ) if (balance right) <= 0) return leftRotate(root); if (balance right)> 0) ( root->right = rightRotate(root->right); return leftRotate(root); ) return root; ) // Print the tree void printPreOrder(struct Node *root) ( if (root != NULL) ( printf("%d ", root->key); printPreOrder(root->left); printPreOrder(root->right); ) ) int main() ( struct Node *root = NULL; root = insertNode(root, 2); root = insertNode(root, 1); root = insertNode(root, 7); root = insertNode(root, 4); root = insertNode(root, 5); root = insertNode(root, 3); root = insertNode(root, 8); printPreOrder(root); root = deleteNode(root, 3); printf("After deletion: "); printPreOrder(root); return 0; )
// AVL tree implementation in C++ #include using namespace std; class Node ( public: int key; Node *left; Node *right; int height; ); int max(int a, int b); // Calculate height int height(Node *N) ( if (N == NULL) return 0; return N->height; ) int max(int a, int b) ( return (a> b) ? a : b; ) // New node creation Node *newNode(int key) ( Node *node = new Node(); node->key = key; node->left = NULL; node->right = NULL; node->height = 1; return (node); ) // Rotate right Node *rightRotate(Node *y) ( Node *x = y->left; Node *T2 = x->right; x->right = y; y->left = T2; y->height = max(height(y->left), height(y->right)) + 1; x->height = max(height(x->left), height(x->right)) + 1; return x; ) // Rotate left Node *leftRotate(Node *x) ( Node *y = x->right; Node *T2 = y->left; y->left = x; x->right = T2; x->height = max(height(x->left), height(x->right)) + 1; y->height = max(height(y->left), height(y->right)) + 1; return y; ) // Get the balance factor of each node int getBalanceFactor(Node *N) ( if (N == NULL) return 0; return height(N->left) - height(N->right); ) // Insert a node Node *insertNode(Node *node, int key) ( // Find the correct postion and insert the node if (node == NULL) return (newNode(key)); if (key key) node->left = insertNode(node->left, key); else if (key> node->key) node->right = insertNode(node->right, key); else return node; // Update the balance factor of each node and // balance the tree node->height = 1 + max(height(node->left), height(node->right)); int balanceFactor = getBalanceFactor(node); if (balanceFactor> 1) ( if (key left->key) ( return rightRotate(node); ) else if (key> node->left->key) ( node->left = leftRotate(node->left); return rightRotate(node); ) ) if (balanceFactor node->right->key) ( return leftRotate(node); ) else if (key right->key) ( node->right = rightRotate(node->right); return leftRotate(node); ) ) return node; ) // Node with minimum value Node *nodeWithMimumValue(Node *node) ( Node *current = node; while (current->left != NULL) current = current->left; return current; ) // Delete a node Node *deleteNode(Node *root, int key) ( // Find the node and delete it if (root == NULL) return root; if (key key) root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key); else if (key> root->key) root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key); else ( if ((root->left == NULL) || (root->right == NULL)) ( Node *temp = root->left ? root->left : root->right; if (temp == NULL) ( temp = root; root = NULL; ) else *root = *temp; free(temp); ) else ( Node *temp = nodeWithMimumValue(root->right); root->key = temp->key; root->right = deleteNode(root->right, temp->key); ) ) if (root == NULL) return root; // Update the balance factor of each node and // balance the tree root->height = 1 + max(height(root->left), height(root->right)); int balanceFactor = getBalanceFactor(root); if (balanceFactor> 1) ( if (getBalanceFactor(root->left)>= 0) ( return rightRotate(root); ) else ( root->left = leftRotate(root->left); return rightRotate(root); ) ) if (balanceFactor right) right = rightRotate(root->right); return leftRotate(root); ) ) return root; ) // Print the tree void printTree(Node *root, string indent, bool last) ( if (root != nullptr) ( cout << indent; if (last) ( cout << "R----"; indent += " "; ) else ( cout << "L----"; indent += "| "; ) cout right, indent, true); ) ) int main() ( Node *root = NULL; root = insertNode(root, 33); root = insertNode(root, 13); root = insertNode(root, 53); root = insertNode(root, 9); root = insertNode(root, 21); root = insertNode(root, 61); root = insertNode(root, 8); root = insertNode(root, 11); printTree(root, "", true); root = deleteNode(root, 13); cout << "After deleting " << endl; printTree(root, "", true); )
Complessità di diverse operazioni su un albero AVL
| Inserimento | Cancellazione | Ricerca |
| O (log n) | O (log n) | O (log n) |
Applicazioni ad albero AVL
- Per l'indicizzazione di record di grandi dimensioni nei database
- Per la ricerca in database di grandi dimensioni








